PacketDetective Lab
CyberDefenders Network Forensics Lab

Scenario
In September 2020, your SOC detected suspicious activity from a user device, flagged by unusual SMB protocol usage. Initial analysis indicates a possible compromise of a privileged account and remote access tool usage by an attacker.
Your task is to examine network traffic in the provided PCAP files to identify key indicators of compromise (IOCs) and gain insights into the attacker’s methods, persistence tactics, and goals. Construct a timeline to better understand the progression of the attack by addressing the following questions.
Question 1
The attacker’s activity showed extensive SMB protocol usage, indicating a potential pattern of significant data transfer or file access. What is the total number of bytes of the SMB protocol?
Answer 1
Looking at the statistics in Wireshark I was able to determine the total amount of bytes used by the SMB protocol was 4406.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 2
Authentication through SMB was a critical step in gaining access to the targeted system. Identifying the username used for this authentication will help determine if a privileged account was compromised. Which username was utilized for authentication via SMB?
Answer 2
Looking through the packets I found an AUTH request in packet 5, using the username Administrator.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 3
During the attack, the adversary accessed certain files. Identifying which files were accessed can reveal the attacker’s intent. What is the name of the file that was opened by the attacker?
Answer 3
The attacker makes a request to open the file eventlog, seen in packet 9.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 4
Clearing event logs is a common tactic to hide malicious actions and evade detection. Pinpointing the timestamp of this action is essential for building a timeline of the attacker’s behavior. What is the timestamp of the attempt to clear the event log? (24-hour UTC format)
Answer 4
A quick search for a clear log request revealed the time and date to be the following:
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 5
The attacker used “named pipes” for communication, suggesting they may have utilized Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) for lateral movement across the network. RPC allows one program to request services from another remotely, which could grant the attacker unauthorized access or control. What is the name of the service that communicated using this named pipe?
Answer 5
I was unfamiliar with named pipes in regards to Windows. So I did require a hint. The following command can be used to isolate the use of named pipes in Wireshark:
Then searching through the packet I was able to determine the service the attacker used was atsvc.

Question 6
Measuring the duration of suspicious communication can reveal how long the attacker maintained unauthorized access, providing insights into the scope and persistence of the attack. What was the duration of communication between the identified addresses 172.16.66.1 and 172.16.66.36?
Answer 6
Looking at both the first and last packet and calculating the difference in timestamps led me to the answer of: 11.7247.
Question 7
The attacker used a non-standard username to set up requests, indicating an attempt to maintain covert access. Identifying this username is essential for understanding how persistence was established. Which username was used to set up these potentially suspicious requests?
Answer 7
Finding this was rather simple. Looking for an NTLMSSP_AUTH request it was clear that the attacker wanted to set up another account called backdoor.

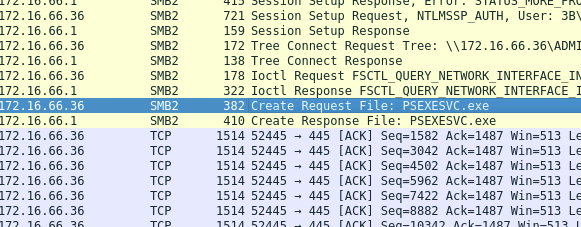
Question 8
The attacker leveraged a specific executable file to execute processes remotely on the compromised system. Recognizing this file name can assist in pinpointing the tools used in the attack. What is the name of the executable file utilized to execute processes remotely?
Answer 8
A quick look at different requests and responses found that a file named PSEXESVC.exe was used by the attacker.

Last updated