HawkEye Lab
CyberDefenders Network Forensics Lab

Scenario
An accountant at your organization received an email regarding an invoice with a download link. Suspicious network traffic was observed shortly after opening the email. As a SOC analyst, investigate the network trace and analyze exfiltration attempts.
Question 1
How many packets does the capture have?
Answer 1
Simply looking at the very last packets number, I can see that there are 4003 packets.

Question 2
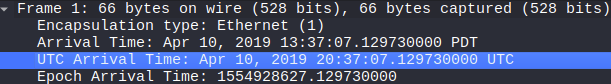
At what time was the first packet captured?
Answer 2
Looking at the UTC arrival time of the first packet, under Frame 1. You can see the packet arrived at the following time and date:
Question 3
What is the duration of the capture?
Answer 3
My comparing the UTC timestamp of the first packet to the last one, gave me the answer: 01:03:41

Question 4
What is the most active computer at the link level?
Answer 4
By looking up the various IP addresses in the packet, I could see that 10.4.10.132 seemed to be the most active. With 49.8% of the captures packets belonging to that single computer. Then I looked for the MAC address of said machine. Giving me the answer:
Question 5
Manufacturer of the NIC of the most active system at the link level?
Answer 5
The answer lies next to the MAC address of the machine. Hewlett-Packard.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 6
Where is the headquarter of the company that manufactured the NIC of the most active computer at the link level?
Answer 6
A quick search online, lead me to their Wikipedia page. Palo Alto.

Question 7
The organization works with private addressing and netmask /24. How many computers in the organization are involved in the capture?
Answer 7
This one tripped me up slightly. Looking up the endpoints menu in Wireshark it revealed 4 private IP addresses, starting with 10.

The last IP address in this list, 10.4.10.255, is the broadcast address. To add to this, private IP addresses follow the address scheme in this image:

I must admit while I am very familiar with IP address ranges start with 192.168, I was unfamiliar with 10.0 and 172.16 ranges.
The answer to this question is 3.
Question 8
What is the name of the most active computer at the network level?
Answer 8
Finding a DHCP packet from the most common IP address in the capture was going to give me the answer. A DHCP packet will contain the hosts name.

Question 9
What is the IP of the organization’s DNS server?
Answer 9
Knowing that the IP address 10.4.10.132 was a standalone machine I used the following command to filter down to any DNS requests that it might make:
Giving me the following result:

The IP address I filtered with was making a ton of internal DNS requests to a single IP address. Therefore the answer to this question being:
Question 10
What domain is the victim asking about in packet 204?
Answer 10
Keeping the same filter as above, you can see the domain the victim was reaching out to was proforma-invoices.com.

Question 11
What is the IP of the domain in the previous question?
Answer 11
The above screenshot reveals that the response back from the URL gave us an IP address.
Question 12
Indicate the country to which the IP in the previous section belongs.
Answer 12
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 13
What operating system does the victim’s computer run?
Answer 13
Knowing that a HTTP request uses a User-Agent field which tracks the OS used by the sender. I was able to find the underlying OS the victim was using, as well as plenty of other data on them.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 14
What is the name of the malicious file downloaded by the accountant?
Answer 14
The same packet in the screenshot above shows the HTTP request and download of the malicious file.
Question 15
What is the md5 hash of the downloaded file?
Answer 15
Using the following filter, then exporting the files via Wireshark.
I was able to extract the file and upload it to VirusTotal.
WORD OF WARNING: If you are following this, de-fang the file. Remove the .exe extension from the end. Although you should be running all this in a Kali VM. Its better to be safe that sorry.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 16
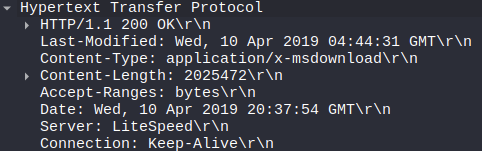
What software runs the webserver that hosts the malware?
Answer 16
Filtering once again for http requests. There was one response from the websever that hosted the malware. After finding the packet, I took a look at the data to find LiteSpeed was the software they were running.
Question 17
What is the public IP of the victim’s computer?
Answer 17
This one I also found a little tricky. Not knowing extactly what to look for after looking up HTTP requests. The key is to find a response from a external IP address. The looking at the Line-based text data field.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 18
In which country is the email server to which the stolen information is sent?
Answer 18
Filtering for SMTP protocols was required to find the IP address of the email server. Leading me to discover its location being the USA.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Question 19
Analyzing the first extraction of information. What software runs the email server to which the stolen data is sent?
Answer 19
Filtering the packet capture to SMTP I was able to find a lot of chatter between the victim and the email server in which the data was exfiltrated. This included the version of software the server was running: Exim 4.91.
Press enter or click to view image in full size

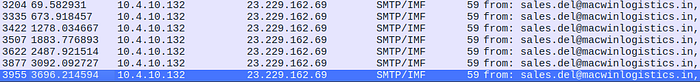
Question 20
To which email account is the stolen information sent?
Answer 20
Looking for specific emails that were sent to the email server. By filtering for SMTP/IMF. I was able to track down 7 emails. Giving me the email address.

Question 21
What is the password used by the malware to send the email?
Answer 21
A quick look through the SMTP packets once again shows the base64 encoded password sitting there. Then after copying it over to cyberchef, I was able to extract the password.

Question 22
Which malware variant exfiltrated the data?
Answer 22
When the malware was crafting the emails, it left its name/signature in the body of the email.

Question 23
What are the bankofamerica access credentials? (username:password)
Answer 23
A plaintext version of the password can be found in the same packet as the above screenshot. Along with many more, extracted from various locations on the victims PC.
Question 24
Every how many minutes does the collected data get exfiltrated?
Answer 24
Looking at the intervals of time in between each email, its clear that the malware extracts the data every 10 mins.
(A small note, the question is not worded properly.)
Press enter or click to view image in full size

Last updated