LGDroid Lab
CyberDefenders Endpoint Forensics
Scenario
On May 21, 2021, an intelligence agency intercepted a mobile device suspected of covert operations. The forensic team performed a full disk dump, extracting databases, logs, and application activity. Findings suggest encrypted communications, anonymous browsing, and unauthorized data transfers. Analyze extracted data to determine suspect activities, network connections, and security risks while establishing a timeline of events.
Question 1
What is the email address of Zoe Washburne?
Answer 1
The first place I would normally check would be contacts. Most phones have a user contact which stores a lot of information about the user of the phone. So opening up contacts3.db, I was able to find the email address along with more information that might be valuable later on.

Question 2
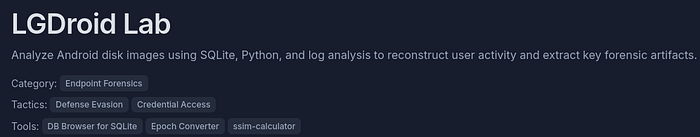
What was the device’s DateTime in UTC at the time of acquisition?
Answer 2
Looking through some of the provided files, a Live Data folder seemed most interesting. Inside there happened to be a .txt file that contained the date and time in which the capture was taken.
Question 3
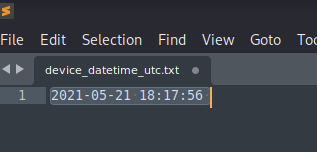
What time was the Tor Browser downloaded in UTC?
Answer 3
Within the same folder as the contacts datebase there happened to be a download.db file. A quick look over said file led me to find the exact timestamp in which the Tor Browser was download. I then had to convert it using a free online conversion tool.
Question 4
At what time did the phone reach a 100% charge after the last reset?
Answer 4
Looking through the Dumpsys folder, I found a couple of .txt files that were battery related. The one named batterystats.txt was the most useful. Looking at the first few lines of the file I could see that the reset time was:
The scrolling down I found the point in which it reached 100% after being plugged in.
5 minutes and 1 second after the reset. So some simple addition of the time at restart and 5 mins and 1 second gave me the answer.
Question 5
What is the password for the most recently connected WIFI access point?
Answer 5
This one was a little tricky. All the files that had WiFi in the name didn’t have any indication as to the password of the various networks that the user had come into contact/connected to. Each one saying <removed>.
So looking deeper in to the file system, I found a folder called com.android.providers.settings. Which gave me the following WiFi password:

Question 6
What app was the user focused on at 2021–05–20 14:13:27?
Answer 6
A handy file named usage_stats.txt gave me a full timeline of what app was accessed by the user and when.
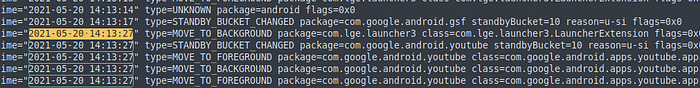
Giving me a clear answer, YouTube.
Question 7
How long did the suspect watch YouTube on 2021–05–20?
Answer 7
Looking at the same file, you are able to tell where the app is being used on the screen. Either the foreground or the background. The user started to watch YouTube at 14:13:27 and moved it to the background at 22:47:57.


8 Hours and 34 Minutes.
Question 8
What is the structural similarity metric for the image “suspicious.jpg” compared to a visually similar image taken with a mobile phone?
Answer 8
Using this website, I am able to tell how similar the images are.

The one taken by the user was stored in the DCIM folder on both the SD card and the main android file system.
Last updated